端午节比赛
题目不难 尽情享受
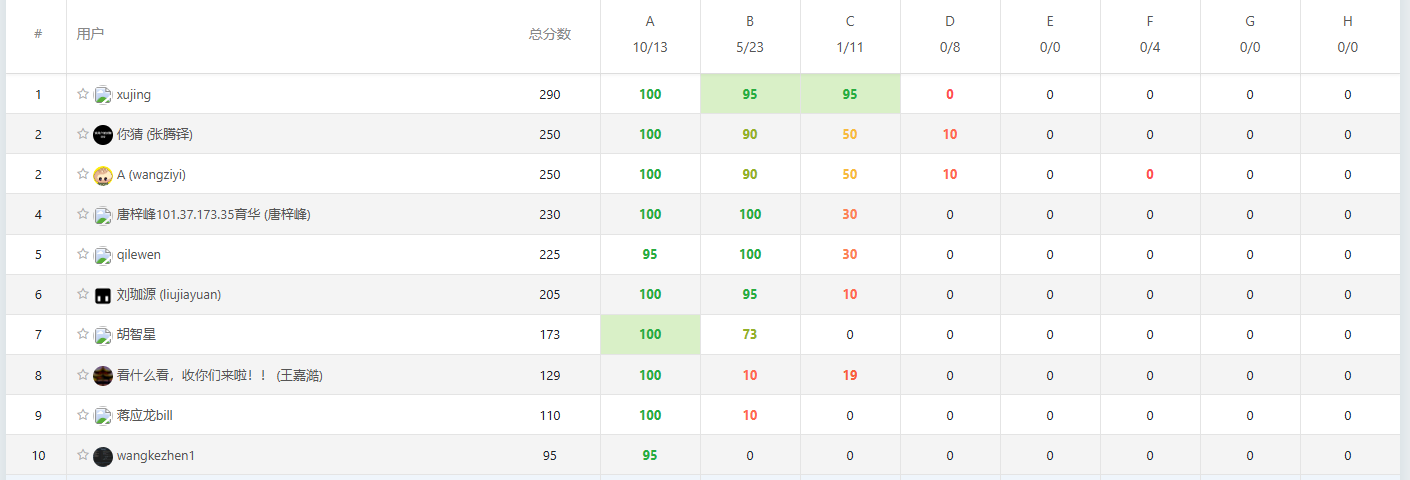
T1
基础模拟题,模拟100次倒水即可,每次倒水都是从一个杯子倒到另一个杯子, 所以我们可以用一个数组来表示每个杯子的水量,然后模拟100次倒水即可.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int s[4], x[4];
void pour(int a, int b) {
// 计算可以倒的水量
int am = min(x[a], s[b] - x[b]);
x[a] -= am;
x[b] += am;
}
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
cin >> s[i] >> x[i];
}
// 模拟100次倒水
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
int from = (i - 1) % 3 + 1;
int to = i % 3 + 1;
pour(from, to);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
cout << x[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
T2
打暴力,依次处理第i个礼物打折的情况,显然处理次数是, 每一次处理的时候都有一个排序 ,时间复杂度是, 所以时间复杂度是,基于,所以可以通过. 此题还有优化的空间,请同学自行思考.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010; // 最大朋友数+10
int n;
long long s;
long long a[N], b[N], c[N];
int main() {
cin >> n >> s;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
}
int nmax = 0;
// 依次处理第i个礼物打折的情况
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (j == i) {
c[j] = a[j] / 2 + b[j]; // 当前礼物打五折
}
else {
c[j] = a[j] + b[j];
}
}
sort(c + 1, c + 1 + n);
long long sum = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= n && sum < s; k++) {
sum += c[k];
if (sum <= s) {
nmax = max(nmax, k);
}
}
}
cout << nmax << endl;
return 0;
}
T3
BFS 解法
BFS 解法的核心思想是,每次从队列中取出一个状态,然后尝试所有可能的操作,将新的状态加入队列中。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110; // 最大杯子容量+10
int steps[N][N] ,vis[N][N];
int x, y, c, n;
int ans = INT_MAX;
// pair<int,int> 约等于以下结构体
// struct pair{
// int first;
// int second;
// }
void bfs() {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({0, 0});
vis[0][0] = 1;
steps[0][0] = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// 计算当前差值
int sum = curr.first + curr.second;
int diff = abs(sum - n);
ans = min(ans, diff);
// 步数满了 就不用继续了
if(steps[curr.first][curr.second] >= c) {
continue;
}
// 操作1: 装满A
if (!vis[x][curr.second]) {
vis[x][curr.second] = 1;
steps[x][curr.second] = steps[curr.first][curr.second] + 1;
q.push({x, curr.second});
}
// 操作2: 装满B
if (!vis[curr.first][y]) {
vis[curr.first][y] = 1;
steps[curr.first][y] = steps[curr.first][curr.second] + 1;
q.push({curr.first, y});
}
// 操作3: A倒入B
int pour = min(curr.first,y - curr.second);
if (!vis[curr.first - pour][curr.second + pour]) {
vis[curr.first - pour][curr.second + pour] = 1;
steps[curr.first - pour][curr.second + pour] = steps[curr.first][curr.second] + 1;
q.push({curr.first - pour, curr.second + pour});
}
// 操作4: B倒入A
pour = min(curr.second, x - curr.first);
if (!vis[curr.first + pour][curr.second - pour]) {
vis[curr.first + pour][curr.second - pour] = 1;
steps[curr.first + pour][curr.second - pour] = steps[curr.first][curr.second] + 1;
q.push({curr.first + pour, curr.second - pour});
}
// 操作5: 清空A
if (!vis[0][curr.second]) {
vis[0][curr.second] = 1;
steps[0][curr.second] = steps[curr.first][curr.second] + 1;
q.push({0, curr.second});
}
// 操作6: 清空B
if (!vis[curr.first][0]) {
vis[curr.first][0] = 1;
steps[curr.first][0] = steps[curr.first][curr.second] + 1;
q.push({curr.first, 0});
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> x >> y >> c >> n;
bfs();
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
DFS 解法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110; // 最大杯子容量+10
// steps[i][j] 表示 杯子A容量为i,杯子B容量为j 时,所需的最小步数
// 初始化为INT_MAX
int steps[N][N] ;
int x, y, c, n;
int ans = INT_MAX;
void dfs(int a,int b,int step) {
if (step > c) {
return;
}
if (step >= steps[a][b]) {
return;
}
steps[a][b] = step;
ans = min (ans, abs(a + b - n));
// 操作1: 装满A
dfs(x, b, step + 1);
// 操作2: 装满B
dfs(a, y, step + 1);
// 操作3: A倒入B
int pour = min(a,y - b);
dfs(a - pour, b + pour, step + 1);
// 操作4: B倒入A
pour = min(b, x - a);
dfs(a + pour, b - pour, step + 1);
// 操作5: 清空A
dfs(0, b, step + 1);
// 操作6: 清空B
dfs(a, 0, step + 1);
}
int main() {
cin >> x >> y >> c >> n;
for (int i = 0; i <= x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= y; j++) {
steps[i][j] = INT_MAX;
}
}
dfs(0,0,0);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
T4
一、问题分析
本题要求将 名同学分批次过河,每次过河的时间由船上的同学数量决定。每次过河后若需返回接下一批同学,需额外花费 分钟返回时间。目标是找到一种分批次方案,使得总时间最少。
关键条件:
- 载 名同学的过河时间为 ,记为 。
- 每次返回需花费 分钟,最后一批无需返回。
二、动态规划解法
1. 状态定义
设 表示将前 名同学送到对岸的最少总时间。
2. 转移方程
对于第 名同学,考虑最后一批载 名同学(),则前 名同学已用 时间送达。此时需:
- 前 名同学分批次过河后,最后一次返回接第 至 名同学。
- 最后一批 名同学过河时间为 ,返回次数取决于前 名同学的批次。
转移逻辑: 若最后一批载 名同学,则前 名同学的过河过程需返回 次。但更简单的方式是,假设前 名同学已全部过河,此时老师在对岸,需返回一次接下一批(除最后一批外,每批过河后需返回一次)。因此,总时间为: [ dp[i] = \min_{k=1}^i \left{ dp[i-k] + T \times \text{返回次数} + f(k) \right} ] 其中,返回次数等于前 名同学的过河批次减一。但更高效的方式是,注意到除最后一批外,每批过河后需返回一次,因此前 名同学的过河总时间中已包含返回时间,而当前转移只需考虑从对岸返回接 名同学的一次返回(若 )。
简化转移方程:
当 时(一次运完),总时间为 。
当 时,需从对岸返回一次接 名同学,因此总时间为:
[
dp[i] = \min(dp[i], dp[i-k] + T + f(k))
]
其中, 为返回时间, 为运送 名同学的时间。
3. 预处理前缀和
为快速计算 ,预处理 的前缀和数组 sum,其中 sum[k] = X_1 + X_2 + \cdots + X_k,则:
[
f(k) = T + sum[k]
]
三、代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int X[2520],n,t;
int presum[2520];
int dp[2520];
int main() {
cin >> n >> t;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> X[i];
}
// 预处理前缀和
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
presum[i] = presum[i-1] + X[i];
}
dp[0] = 0; // 0名同学用时0
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
// 前i名一次性运过去
dp[i] = presum[i] + t;
// 最后一批载k名同学,k从1到i-1 (k == i 时,表示前i名一次性运过去)
for (int k = 1; k <= i-1; ++k) {
dp[i] = min( dp[i], dp[i-k] + presum[k] + t + t);
}
}
cout << dp[n] << endl;
return 0;
}
T5
一、问题分析
本题要求在数轴上选择一个点,使得最多的区间包含该点。这是一个典型的区间覆盖问题,核心是找到一个点,使其被最多的区间同时覆盖。
二、算法思路
-
事件点法:
- 将所有区间的左端点和右端点视为“事件点”,并记录每个事件点的类型(左端点或右端点)。
- 对事件点进行排序,排序规则为:
- 左端点在前,右端点在后(若坐标相同,左端点优先,因为左端点代表区间开始,右端点代表区间结束)。
- 坐标相同的左端点或右端点,顺序不影响结果(可任意排列)。
- 遍历排序后的事件点,用计数器
cnt记录当前覆盖的区间数。每当遇到左端点时,cnt加1;遇到右端点时,cnt减1。在遍历过程中,记录cnt的最大值,即为最多被覆盖的区间数。
-
排序的关键:
- 左端点必须在右端点之前处理,以确保在区间的起点处及时增加覆盖计数,在终点处减少覆盖计数。这样可以保证在区间内部的所有点都能被正确统计到最大覆盖数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50050; // 最大户数+50
struct Node {
int p;
int v; // 0表示一件事情发生,1表示一件事情结束
bool operator<(const Node& other) const {
if (p == other.p) {
return v < other.v;
}
return p < other.p;
}
};
Node a[N * 2];
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n * 2; i += 2) {
cin >> a[i].p >> a[i + 1].p;
a[i].v = 0;
a[i + 1].v = 1;
}
sort(a + 1, a + n*2 + 1);
int ans = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n*2; i++) {
if (a[i].v == 0) {
cnt++;
ans = max(ans, cnt);
}else {
cnt--;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
T6
题目显然只要求出有多少种不同的斜率即可,所以我们只要暴力求出所有斜率,然后去重.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 210; // 最大点数+10
struct Point {
int x, y;
} p[N];
// 斜率
struct Node {
int dx, dy; // 保证dx >= 0;
bool operator<(const Node &t) const {
return dy * t.dx < t.dy * dx;
}
bool operator!=(const Node &t) const {
return dy * t.dx != t.dy * dx;
}
};
Node a[N*N];
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
}
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = i+1; j <= n; j++) {
a[++cnt].dx = p[j].x - p[i].x;
a[cnt].dy = p[j].y - p[i].y;
if (a[cnt].dx < 0) {
a[cnt].dx = -a[cnt].dx;
a[cnt].dy = -a[cnt].dy;
}
}
}
sort(a+1, a+1+cnt);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
if (i == 1 || a[i] != a[i-1]) {
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
T7
一道简单的最短路问题,唯一要注意的是因为查询多次,我们要预处理好从所有点出发的最短路情况才能保证不超时.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 310; // 最大城市数+10
int n, q;
int a[N];
string s[N];
vector<int> g[N];
struct Node {
long long steps, sum;
bool operator<(const Node& other) const {
return steps < other.steps || (steps == other.steps && sum > other.sum);
}
};
// 从每个点出发的最短路数据
Node node[550][550];
void bfs(int u) {
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
node[u][i] = {LLONG_MAX, 0};
}
node[u][u] = {0, a[u]};
queue<int> q;
q.push(u);
while(!q.empty()) {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0;i < g[t].size();i++) {
int v = g[t][i];
if(node[u][v].steps > node[u][t].steps + 1) {
node[u][v] = {node[u][t].steps + 1, node[u][t].sum + a[v]};
q.push(v);
}else if(node[u][v].steps == node[u][t].steps + 1) {
if(node[u][v].sum < node[u][t].sum + a[v]){
node[u][v] = {node[u][t].steps + 1, node[u][t].sum + a[v]};
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> s[i];
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if(s[i][j-1] == 'Y') g[i].push_back(j);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
bfs(i);
}
cin >> q;
while(q--) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
Node res = node[u][v];
if(res.steps == LLONG_MAX) {
cout << "Impossible\n";
} else {
cout << res.steps << " " << res.sum << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
T8
可以用线段树或者分块解决,由于数据不大也可以优化暴力,请多思考一会儿
- 状态
- 已结束
- 规则
- 乐多
- 题目
- 8
- 开始于
- 2025-5-31 8:30
- 结束于
- 2025-6-2 20:30
- 持续时间
- 60 小时
- 主持人
- 参赛人数
- 19
